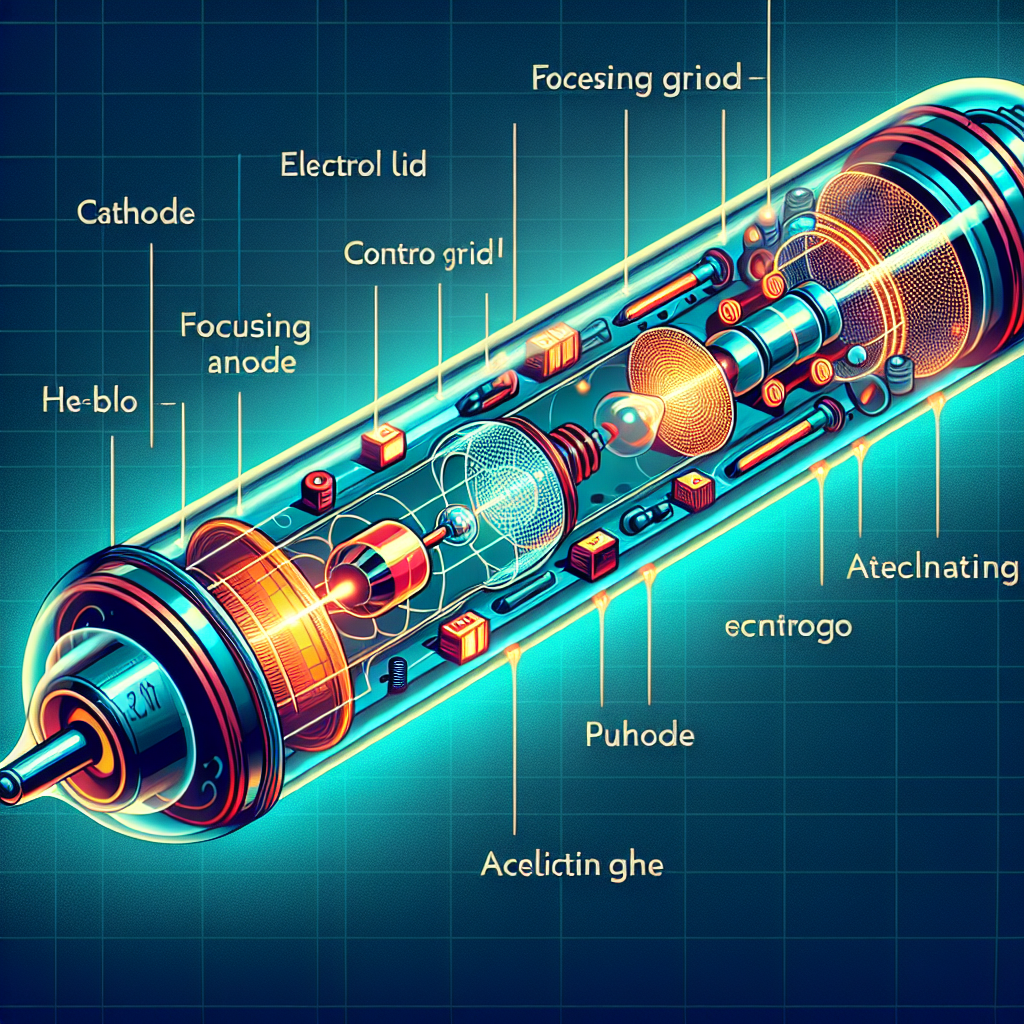
Understanding the Electron Gun in a CRT
The electron gun is a crucial component in a Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT) that plays a vital role in displaying images on a screen. This device is key to the function of CRT technology, which was once the backbone of television and computer monitor displays. To better understand the electron gun, let’s dive into its components, mechanisms, and applications.
Components of an Electron Gun
The electron gun consists of several parts that work together to generate and focus an electron beam. The primary components are:
- Cathode: Emits electrons when heated.
- Control Grid: Modulates the flow of electrons.
- Accelerating Anode: Speeds up the electrons towards the screen.
- Focusing Anode: Focuses the electron beam to a fine point.
- Deflection System: Directs the beam to the correct spot on the screen.
Mechanism of Electron Emission
The electron gun starts with the cathode, which is heated to release electrons through a process known as thermionic emission. These emitted electrons then move through the control grid, accelerating anode, and focusing anode, where their speed and direction are precisely controlled.
Steps in Electron Emission
- Thermionic Emission: The cathode is heated to release electrons.
- Acceleration: The control grid controls electron flow while the accelerating anode increases their speed.
- Focusing: The focusing anode ensures the electron beam is sharp and focused.
- Deflection: The deflection system moves the beam across the screen to create images.
Applications of Electron Gun in CRT
The electron gun is integral to the operation of CRTs, which have been widely used in:
- Televisions
- Computer Monitors
- Oscilloscopes
- Radar Displays
Tabular Representation: CRT Applications
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Televisions | Used for displaying visual content. |
| Computer Monitors | Used for displaying computer data and graphics. |
| Oscilloscopes | Used in laboratory environments to visualize electrical signals. |
| Radar Displays | Used in navigation and weather forecasting systems. |
Advantages and Limitations
Despite being largely replaced by modern display technologies, CRTs have some advantages and limitations:
- Advantages: High contrast ratios, ability to display different resolutions at optimal quality.
- Limitations: Bulkiness, high power consumption, lower brightness and resolution compared to modern displays.
Evolution and Legacy
Although CRTs are outdated, their technology laid the foundation for modern display technologies. The principles of electron emission and beam deflection are still relevant today in advanced fields such as electron microscopy and particle accelerators.
In summary, the electron gun in a CRT is a vital component setting the groundwork for how images are displayed, greatly impacting television, computing, and various scientific fields.